REFRIGERATOR (SINGLE DOOR)
SINGLE-DOOR REFRIGERATOR: COMPONENTS & WORKING
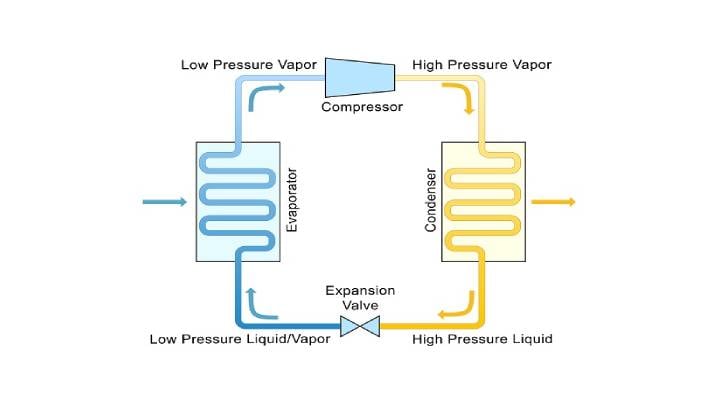
1. Construction & Working of Key Components
(A) Compressor
- The heart of the refrigeration system.
- In single-door refrigerators, typically hermetic reciprocating compressors are used.
- Working:
- Compresses the low-pressure refrigerant vapor.
- Increases its pressure and temperature.
- Sends it to the condenser for heat rejection.
(B) Condenser
- A heat exchanger that removes heat from the refrigerant.
- Types:
- Wire-and-tube type (found at the back of refrigerators).
- Plate type (mounted on the body of the refrigerator).
- Working:
- Converts hot refrigerant vapor into a high-pressure liquid.
- Heat is rejected to the surrounding air.
(C) Capillary Tube
- A thin, long tube that acts as an expansion device.
- Functions:
- Reduces refrigerant pressure.
- Controls the flow of refrigerant to the evaporator.
(D) Evaporator
- Located inside the freezer compartment.
- Working:
- Absorbs heat from stored food.
- Converts liquid refrigerant into low-pressure vapor.
- Refrigerant then returns to the compressor.
(E) Suction Line Heat Exchanger
- Some models use a heat exchanger between the suction line and capillary tube.
- Function:
- Improves cooling efficiency by subcooling the refrigerant.
- Prevents liquid refrigerant from reaching the compressor.
(F) Door & Gaskets
- Door:
- Made of metal or plastic with insulation.
- Gaskets (Rubber Seals):
- Prevent warm air leakage.
- Ensure proper sealing to maintain cooling.
(G) Heat Insulation Materials
- Polyurethane foam (PUF) is commonly used.
- Ensures minimum heat transfer and energy efficiency.
2. Electrical Components
(A) Thermostat
- Controls the temperature by switching the compressor ON/OFF.
- Adjustable knob inside the fridge.
(B) Relay & Overload Protector
- Relay: Provides starting torque to the compressor.
- Overload Protector: Prevents overheating of the compressor.
(C) Defrost Heater & Timer
- Some single-door refrigerators have manual defrosting.
- Automatic defrosting models use a heater and timer.
(D) Interior Light & Door Switch
- Turns ON when the door opens.
3. Flushing, Capillary & Drier Replacement
(A) Flushing Evaporator & Condenser
- Removes dirt, moisture, and impurities.
- Uses refrigerant gas or solvent flushing method.
(B) Replacing Capillary & Drier
- The capillary tube and drier must be replaced when:
- System is clogged due to moisture or oil.
- Capillary tube is damaged (causing improper cooling).
- Drier absorbs excess moisture, reducing efficiency.
4. Evacuation, Leak Testing & Gas Charging
(A) Evacuation (Vacuum Process)
- Removes air and moisture using a vacuum pump.
(B) Leak Testing
- Done using:
- Soap bubble method (for visible leaks).
- Nitrogen pressure test (for precise detection).
(C) Gas Charging Methods
- Refrigerant charging process:
- Weighing method (most accurate).
- Pressure gauge method.
5. Refrigerants Used in Single-Door Refrigerators
Common Refrigerants & Properties
| Refrigerant | Type | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| R-12 | CFC | Older refrigerators (Banned) |
| R-134a | HFC | Most common in older models |
| R-600a | Hydrocarbon | Newer eco-friendly refrigerators |
| R-290 | Hydrocarbon | High-efficiency models |
- Compressor compresses refrigerant gas.
- Condenser releases heat to surroundings.
- Capillary tube regulates refrigerant flow.
- Evaporator absorbs heat from food.
- Flushing & leak testing improve performance.
- Gas charging & proper evacuation ensure cooling efficiency.
- Eco-friendly refrigerants like R-600a are replacing older CFCs and HFCs.
