Drawing Instrument
Drawing Board:
- Drawing Board Provides a stable surface for drawing.
- made of wood or plastic with a smooth finish.
- Parts
- Strips
- 2 Battens
- Ebony Edge
- Drawing board is set with stand at 20 degree angle
- As per SP: 46- 1988 drawing board was represented by B
As per IS 1944- 1989 drawing board is represented by D- D0 : 1500 mm x 1000 mm x 25 mm
- D1 : 1000 mm x 700 mm x 25 mm
- D2 : 700 mm x 500 mm x 15 mm
- D3 : 500 mm x 350 mm x 15 mm
- Drawing board is made of soft wooden platens. A
- A strip of hard ebony edge is fitted up in a groove on the shorter edge of the board and perfectly lined to provide the guide for the T-square.
Drawing Sheet:
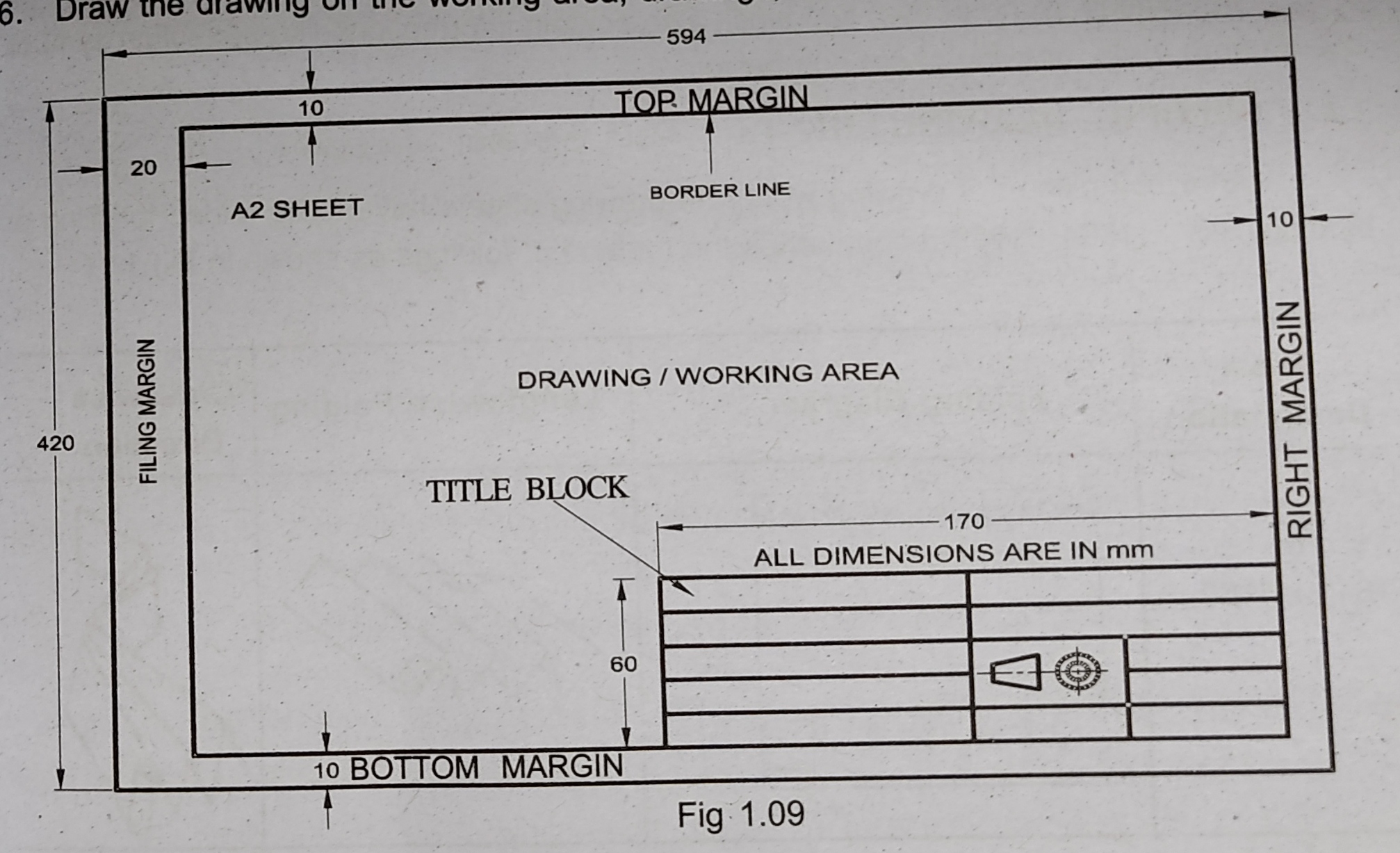
- The drawing sheet consist of drawing space, title block and sufficient margins.
- After fixing the drawing sheet on the drawing board, margins should be drawn.
- A typical drawing sheet is shown in figure and consist of the following:
- Borders – space left all around in between the trimmed edges of the sheet. A minimum of 10 mm
- Filling margin – 20 mm minimum on left hand side with border included. This is provided for taking perforations.
- Title box – The title box is drawn at the bottom right hand corner of every drawing sheet and provides technical and administrative details regarding the drawing/component. Though there are various dimensions for the title box, for Engineering students it is advisable to use a title box of size 170 mm x 65 mm.
- The title box is divided in to two zones:
- (a) part identification zone and
- (b) additional information zone.
- In the part identification zone, information like the component identification number , name of the part, the legal owner of the drawing (i.e. the name of firm/component/etc will be highlighted where as in the additional information zone, technical information like symbols indicating the system of projection, scale of drawing, method of indicating surface texture, geometric tolerances, etc. will be highlighted.
- drawings are prepared by means of pencils or pen.
- Drawing sheets are available in standard sizes as shown in Table .
| size | कटी हुयी शीट की माप (mm) | बिना कटी हुयी शीट की माप (mm) |
| A0 | 841 x 1189 | 880 x 1230 |
| A1 | 594 x 841 | 625 x 880 |
| A2 | 420 x 594 | 450 x 625 |
| A3 | 297 x 420 | 330 x 450 |
| A4 | 210 x 297 | 240 x 330 |
| A5 | 148 x 210 | 165 x 240 |


Mini Drafter :
- Mini Drafter is a device used to draw parallel or inclined lines very effectively with ease.
- This is mounted on the top left corner of the drawing board by means of a clamping mechanism

T-Square:
- T-Square Used to draw horizontal and vertical lines.
- T-square consists of two main parts:
- blade (the long, straight section)
- head (or stock),
- Both attached at a 90-degree angle to the blade.
- Size
- T0 : 1500 ± 10 mm
- T1 : 1000 ± 10 mm
- T2 : 700 ± 5 mm
- T3 : 500 ± 5 mm
Set Squares:
- Set Squares Assist in drawing angles and inclined lines.
- Set squares are a set of 45° set square and 30°-60° set-square
- They are used in conjunction with each other and with T-square to draw parallel, inclined and perpendicular lines.
- They are made of transparent acrylic.
- The 45° set square generally has a protractor where as the 30°-60° set-square includes French curves.

Protractor:
- Protractor Measures angles between lines.

Compass:
- compass Draws circles and arcs.
- Generally two sizes of compasses:
- large compass
- small spring bow compass .
- Each compass consist of a needle point and a pencil point.
- For drawing very large radius arcs, the pencil point leg can be removed from the knee joint and a lengthening bar can be inserted to increase the radius of the arc.

Divider:
- Divider Transfers dimensions and divides lines into equal parts.
- Dividers are used to transfer lengths to the drawings either from scales or from the drawing itself.
- Similar to the compasses, two sizes of dividers are used in technical drawings. One large divider and the other small spring bow divider.

French Curves:
- French curve/Flexible curve Used for drawing smooth curves.
- French curve is free form template make of acrylic and is used to draw a smooth curve passing through a number of points. The outer profile of the French curve is adjusted such the smooth curve passes through more than three points and a curve passing through these lines are drawn. The next part of the curve is then drawn by using the next three points in addition to the last two points of the previous curve.A typical French curve is shown in figure 6.
- A flexible curve is consists of a flexible, generally made of metallic wire coated with a thick rubber material. This can be bend in to any shape so that its working edge can be matched with a number of points and a smooth curve can be .

Pencils:
- Father of Pencil – Conrad Gassner
- hard pencils (H-Grade) – contain more clay and less graphite, making them harder and lighter Colour.
- soft pencils (B-Grade) – contain more graphite and less clay, making them softer and darker/Black.
- 18 Pencil Grades for Engineering Drawing
- Hard Pencils – 9H , 8H, 7H, 6H, 5H, 4H,
- Medium Pencils – 3H, 2H, H, F, HB, B,
- Soft Pencils – 2B, 3B, 4B, 5B, 6B, 7B
- Hard Pencils (H Grades):
- 9H to 4H: These are the hardest pencils, used for light construction lines and guide lines. They produce very light marks and are ideal for creating fine details without smudging.
- Medium Pencils:
- 3H, 2H, H: These are commonly used for general line work, such as drawing borders, centerlines, and construction lines. They provide a good balance between line clarity and erasability24.
- HB, B: This is a versatile pencil used for making notes and drawing visible lines. It offers a moderate line darkness and is suitable for most general drawing purposes.
- F (Fine): Similar to HB but slightly harder, maintaining a fine point and used for detailed work.
- Soft Pencils (B Grades):
- 2B to 7B: These pencils are softer and produce darker lines. They are less commonly used in engineering drawing but can be useful for shading or creating darker tones in artistic aspects of technical drawings
- Eraser and Sharpener:
- Essential for correcting and maintaining pencils.
- CAD Software:
- Modern tool for creating precise digital drawings.
